Table Of Content
- What is SEO Corruption?
- 1. Paid Link Schemes
- 2. Content Manipulation
- 3. Astroturfing
- 4. Link Farming
- Examples of SEO Corruption Signs
- Why This is an Issue
- How Moderators May Misuse Their Power for Swift Deletion or Bans
- How Paid Moderators Get Away with It
- Why This Happens: Power and Lack of Oversight
- Wikipedia’s Response
Corruption of SEO can be defined as the unethical habit of individuals or organizations trying to manipulate the methods of search engine optimization so as to have an impact on the ranking of websites on the list of a certain search engine. A typical manifestation of corruption in SEO can be seen in the ill-conceived habit of high-authority platforms like Wikipedia, whereby some individuals display links or manipulate existing links leading to certain websites with the intent of increasing their ranking in search engines such as Google. This has nothing to do with the usage of AI to generate content that can be more easily found, it’s a very old practice that is there since the page rank algorithm become king and the number of backlinks was all that mattered to rank number one
What is SEO Corruption?
Here’s how SEO corruption might work in the context of high domain authority websites, such as Wikipedia:
1. Paid Link Schemes
High domain authority (DA) websites, like Wikipedia (one of many we take as example in this very page), are very powerful in their influence because search engines believe in them and rank them highly. Certain individuals with editing privileges on such websites may be approached and paid money or lured with other offers to include links to certain websites in the articles themselves. These links, sometimes referred to as “backlinks,” can help improve the target site’s ranking in search engines because search engines like Google consider it a vote of trust from a reputable source.
2. Content Manipulation
In others, editors are paid to write full Wikipedia pages or sections of Wikipedia that speak positively about their website. Such sections are organic in nature but are actually tailor-made for housing backlinks that could help with SEO. This creates an impression of authority and relevance for the website being promoted, even if it doesn’t actually deserve such status.
3. Astroturfing
The search engine optimization corruption on high-authority platforms sometimes involves creating a series of fake accounts or leveraging social networks of editors to support and approve certain changes. In other words, a person may create many different accounts for insertion and maintenance of backlinks or making favorable edits. This will keep him or her out of the sight of moderators on that site. It gives them an aspect of broad consensus or legitimacy, though changes are all part of a well-coordinated scheme to improve SEO.
4. Link Farming
Another pertinent tactic involves “link farming.” In link farming, networks of websites-formerly including high-authority platforms-continually link to each other to manufacture an inflated level of importance for each site. While search engines used to be tricked by this technique, the more sophisticated algorithms currently in use penalize the effort. That being said, some high-DA sites can still be manipulated in this way, with Wikipedia pages becoming nodes within larger link farms.
Examples of SEO Corruption Signs
- Mysterious, unrelated links in articles or academic blogs.
- Articles on high-authority sites containing out-of-place links to commercial websites.
- Sponsored content labeled as “news” but packed with SEO-optimized links.
- Sudden rank boosts for relatively unknown websites, signaling unnatural backlinks.
Why This is an Issue
SEO corruption degrades the integrity of search engines and the platforms being used. This goes against the very mission of Wikipedia to provide neutral information, and it distorts those search engine rankings, which is supposed to denote relevance and authority based upon organic factors, not manipulative schemes.
While high DA/DR websites like Wikipedia actively try to combat such practices by employing editors and bots that monitor for “spammy” links or poor edits, SEO corruption remains a serious issue, especially when utilized to prop up less credible websites for financial gain.
How Moderators May Misuse Their Power for Swift Deletion or Bans
- Selective Enforcement of Guidelines
Wikipedia has very strict rules about notability and the use of reliable sources for creating or maintaining articles. These guidelines can be selectively manipulated by moderators. If an individual tries to create a page about their company but struggles to meet subjective interpretations of Wikipedia’s guidelines (e.g., insufficient media coverage), the moderator can mark the page for “speedy deletion.” This process allows the article to be removed without significant review, often within hours.- Outcome: Honest attempts to document legitimate companies are shut down quickly by citing “self-promotion” or “insufficient notability.”
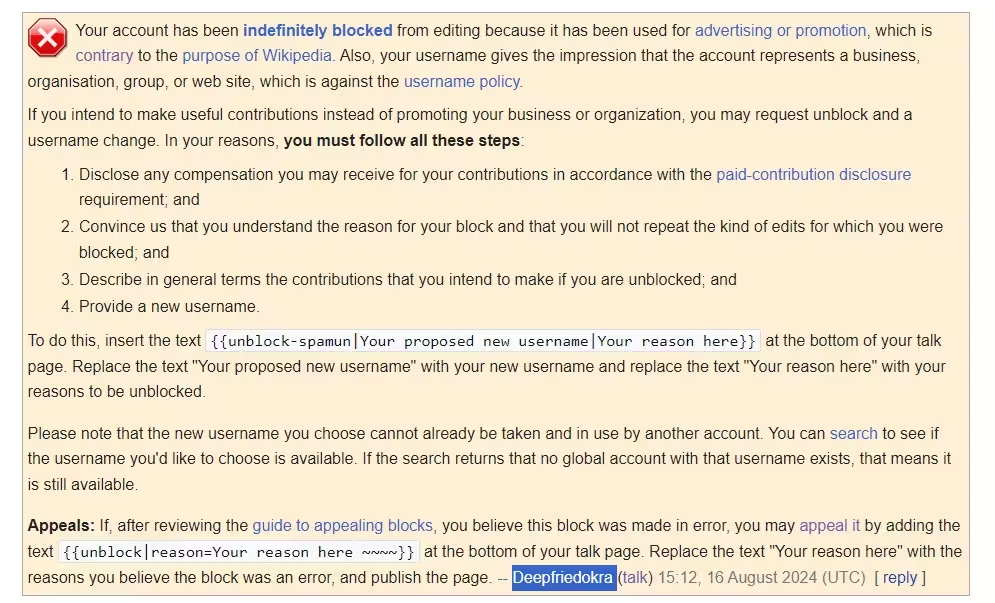
- Outcome: Honest attempts to document legitimate companies are shut down quickly by citing “self-promotion” or “insufficient notability.”
- Indefinite Banning of Editors
If there are repeated attempts to re-add a deleted or declined page, moderators will then block indefinitely editors for Wikipedia’s policy on either spam or disruptive conduct. Even honest, good-faith attempts to meet the standards can be seen to be interpreted as “conflict of interest” editing or promotional activity and permanent bans.
From our experience we got an extremely unfair treatment from an administrator named “YesI’mOnFire” which has a personal page like that:

Wikipedia admins tell that they take promotional editing very seriously, yet most of the organizations have a page on it.
How Paid Moderators Get Away with It
On the flip side, some editors and moderators exploit their knowledge of Wikipedia’s rules for personal gain by accepting payments to create, modify, or protect pages. This behavior is unethical and technically prohibited under Wikipedia’s guidelines, but it’s hard to police. Here’s how it often plays out:
- Backchannel Deals for Page Creation
Certain moderators—often operating covertly—accept payments to create pages for companies or individuals that might not strictly meet notability guidelines. These editors know how to format the pages perfectly to avoid triggering automated flags or deletion.- Outcome: Paid articles for non-notable companies stay up while others with genuine claims are swiftly deleted.
- Protection from Deletion
Some moderators provide “protection services”—for a fee—by monitoring and defending certain pages from being flagged or deleted. They exploit their reputation within Wikipedia’s editorial community to suppress challenges or disguise biased content as neutral. - Suppressing Competing Pages
In more unethical cases, moderators may get paid to target and delete competing companies’ pages while keeping the favored client’s page intact. This suppression can be framed as routine enforcement of Wikipedia’s guidelines, making it hard to detect as foul play.
Why This Happens: Power and Lack of Oversight
- Asymmetry of Power: Established editors and moderators gain reputation and authority on the platform, allowing them to act with minimal oversight. The new or occasional contributors-especially those who might have a vested interest in their company-have little recourse if their efforts are dismissed or banned.
- Anonymity and Lack of Transparency: Many editors operate under pseudonyms; hence, identifying conflicts of interest or holding corrupt moderators accountable is not that easy.
- Demand for Wikipedia Presence: Most firms want to be represented on Wikipedia due to the effects it has on SEO and public perception. This, of course, leads to a lucrative black market for paid edits and page creation.
Wikipedia’s Response
Wikipedia has on paper tried to address these issues with policies like:
- Conflict of Interest Disclosure: Editors with a vested interest are supposed to disclose their affiliations.
- Spam and Paid Editing Detection: Algorithms and volunteer-driven patrols try to spot suspicious activity.
- Arbitration Committees: These committees review and investigate accusations of moderator misconduct, though the process is slow and limited.
None of these, however, are failsafe. The very big size, reliance on volunteers, and decentralized nature make it very hard to avoid all cases of unethical editing or moderators’ abuse on Wikipedia.

